PsychNewsDaily Publishers
100 Summit Drive
Burlington, MA, 01803
Telephone: (320) 349-2484
PsychNewsDaily Publishers
100 Summit Drive
Burlington, MA, 01803
Telephone: (320) 349-2484
A Combat Medic Specialist 68W provides emergency medical care to soldiers in combat and non-combat situations, requiring physical strength, medical knowledge, and quick decision-making skills.
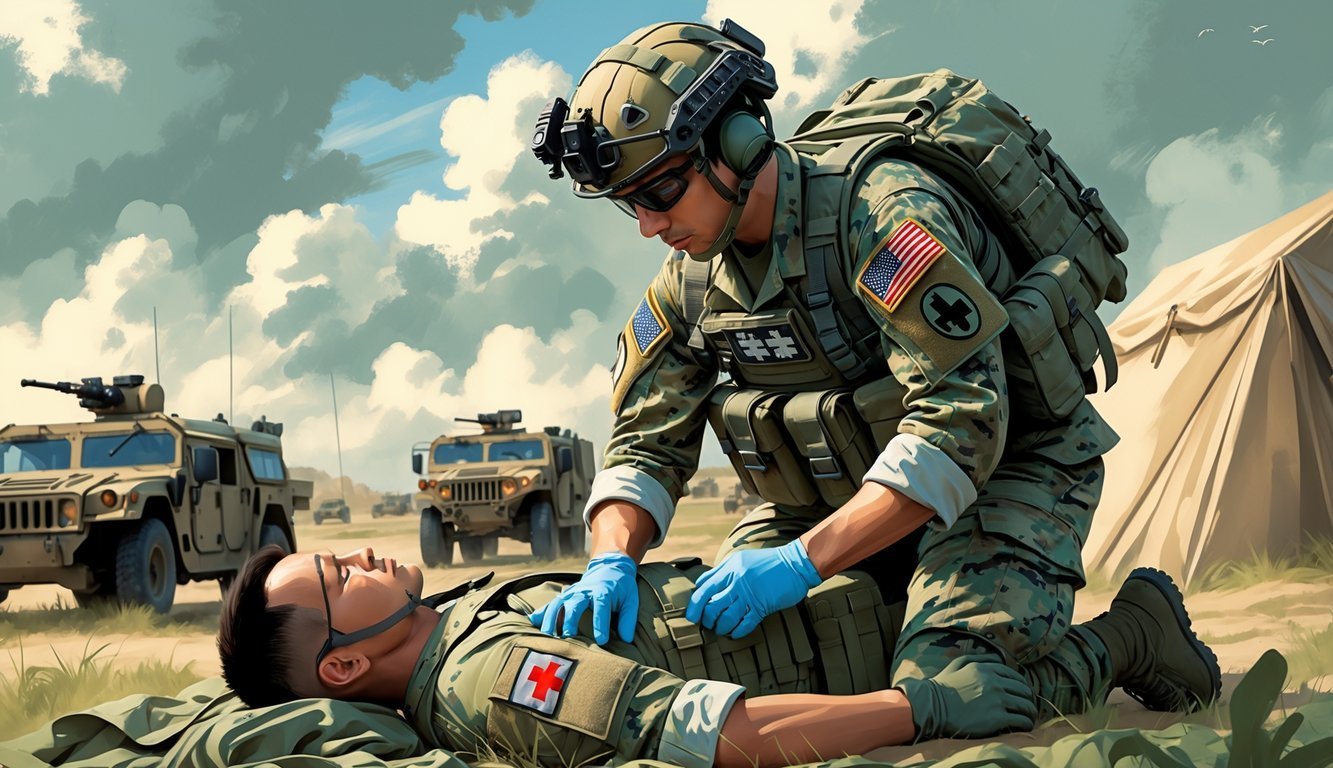
A Combat Medic Specialist 68W steps into a vital role in the Army by giving emergency medical care to soldiers, whether in the middle of combat or during quieter moments. You’ll get trained to perform life-saving treatments right on the battlefield and support your team’s health during missions. This job takes a mix of physical strength and medical know-how, and you’ve got to act fast when things get chaotic.
As a 68W, you usually find yourself as the first responder in some pretty rough environments, offering care that buys time until someone can move the patient to safety. You’ll pick up a whole range of medical skills, from patching up injuries to keeping your unit in good health.
Honestly, the job’s demanding—no sugarcoating that—but it’s also one of the most rewarding things you can do.
If you want a career where you actually make a difference and work closely with your team, the Combat Medic Specialist MOS has some unique challenges and plenty of room for growth.
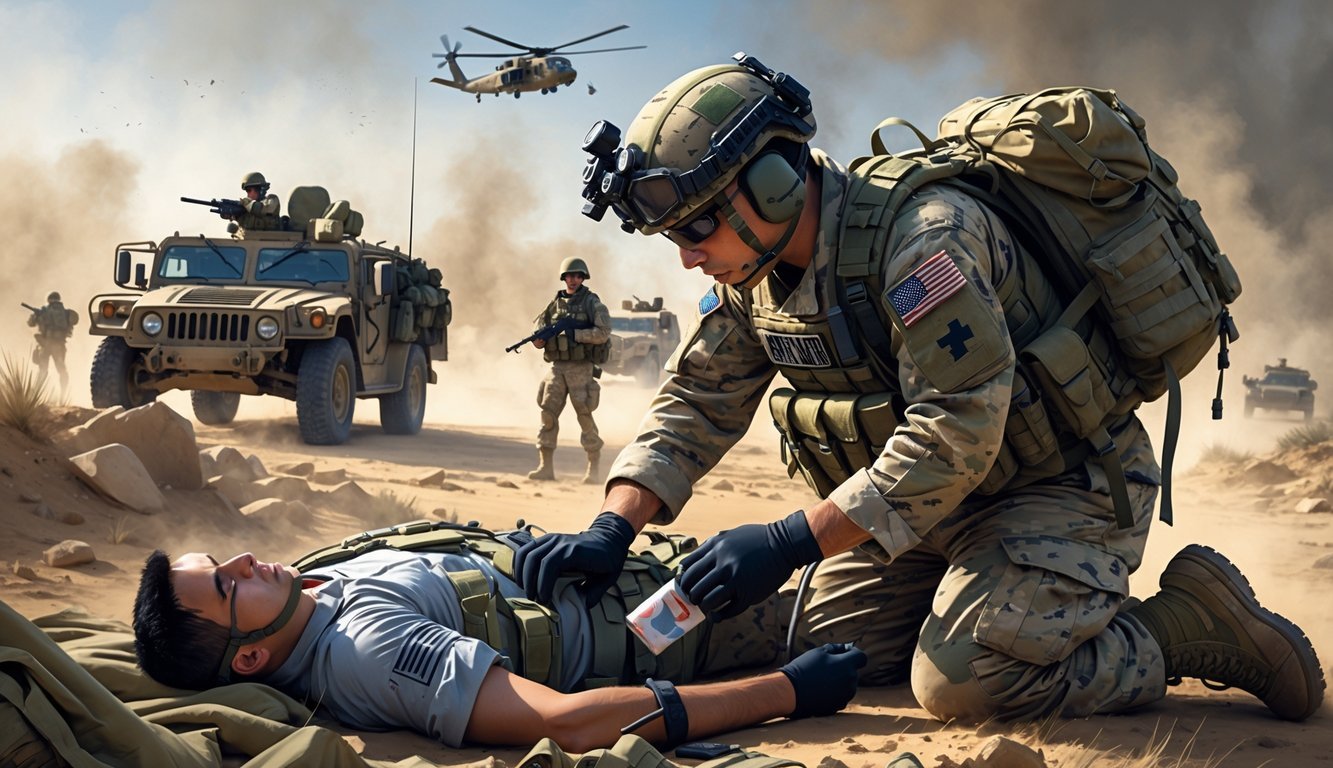

When you become a Combat Medic Specialist (68W), you join a core part of the Army Medical Department. You’ll train to respond fast to injuries in the field and deliver critical care.
To get there, you have to meet eligibility requirements, pass the ASVAB, and finish both basic and specialized training.
The Army calls Combat Medic Specialists by the title 68W. You take on the first responder role in combat and non-combat settings, giving emergency medical treatment and evacuating wounded soldiers.
You help Army units keep going by offering care until soldiers reach a higher level of medical support. The U.S. Army Medical Center of Excellence, under the Army Training and Doctrine Command, oversees your training.
Your job lines up a lot with what civilian paramedics do, but you’ll often find yourself in tougher, riskier conditions. Sometimes you’ll get specialty titles, like Army Medical Department Medic, and your tasks can stretch across all sorts of situations, both on and off the battlefield.
To qualify for 68W, you need to meet the Army’s basic enlistment standards. That means you must fit age, physical fitness, and citizenship requirements, just like any other Army job.
Your recruiter will want your first and last name, birth date, phone number, email address, and zip code.
You’ll have to take the ASVAB test. For 68W, you need at least a 101 in the Skilled Technical (ST) section. Some people qualify with a 107 General Technical (GT) score, but honestly, the ST score lines up better with the medical skills you’ll be learning.
Scoring high enough shows you’ve got the technical and general knowledge you’ll need. If you’re not sure, the Army Career Match quiz might help you figure out if 68W is a good fit before you commit.
Your journey kicks off with 10 weeks of Basic Combat Training (BCT) to build military skills and get you in shape.
After BCT, you move on to 16 weeks of Advanced Individual Training (AIT) at the U.S. Army Medical Center of Excellence.
During AIT, you’ll take the First Responder Training Course and dive into combat casualty care, evacuation procedures, and emergency medical treatment.
This training gets you ready to handle injuries under pressure and in all kinds of environments.
You’ll also practice prolonged casualty care techniques. Field training exercises will test how well you can provide care and work as part of a team.
This hands-on training is what makes you ready to save lives wherever the Army sends you.
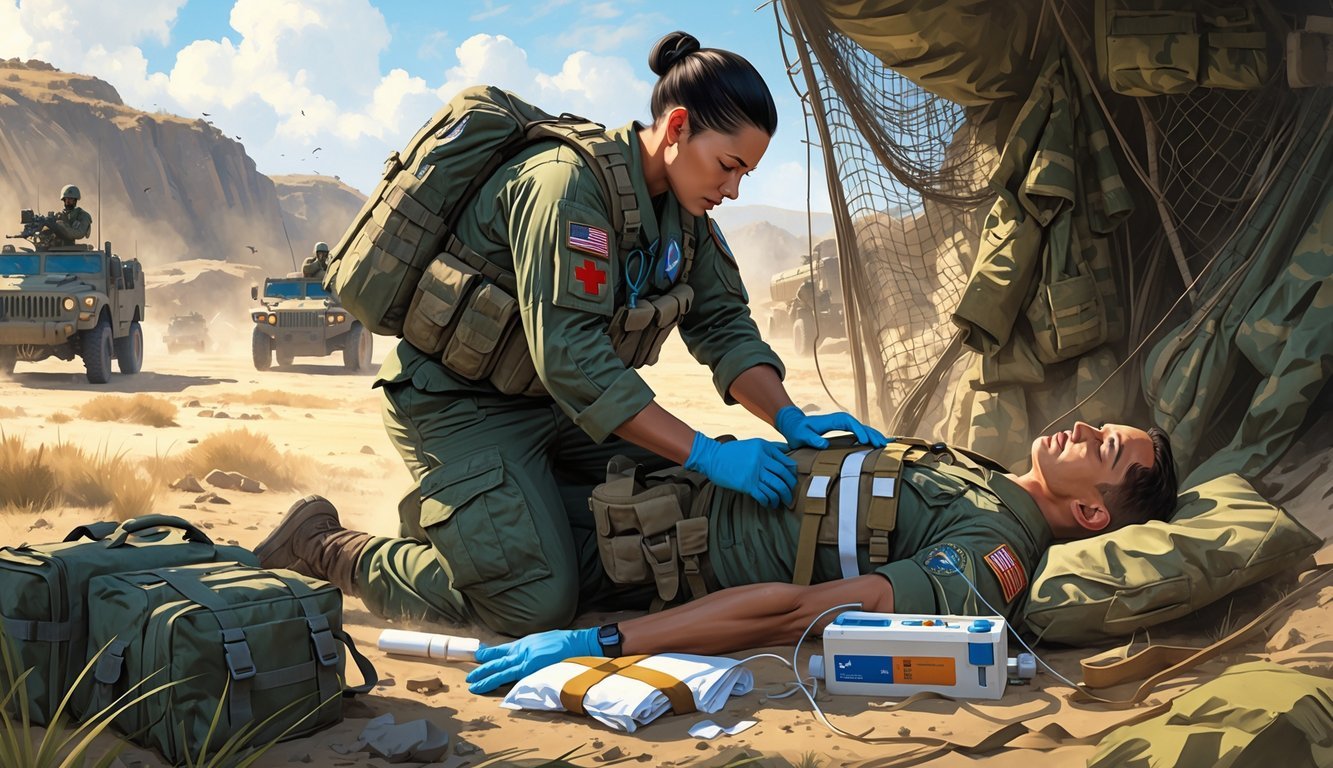

As a combat medic, you step up to save lives on the battlefield. You manage patient care, handle medical supplies, and keep it together under pressure—all while looking out for your fellow soldiers.
Your main job is to give emergency medical care right where soldiers get hurt. That means you have to assess injuries fast and use triage to decide who needs help first.
You’ll handle limited primary care too, like cleaning wounds and stopping infections.
Besides treating battlefield injuries, you’ll help with outpatient care for soldiers recovering from less urgent problems. Sometimes you assist doctors and nurses if they’re around.
Your work keeps your unit healthy and ready for whatever comes next.
You’ll use tactical combat casualty care techniques to manage serious injuries. This covers basic life support, airway management, bleeding control, and treating shock.
Your training prepares you to jump in and act fast, even when things get hectic.
You’ll learn emergency medical techniques similar to those in basic EMT courses. This means patient assessment, clearing airways, and starting evacuation procedures to get wounded soldiers to higher-level care.
You’ve got to stay calm and do your job, even under fire.
You carry and manage vital medical supplies—bandages, splints, tourniquets, and all the essentials. Keeping your gear ready for action is a big part of your job.
Sometimes you help with ambulance operations or set up aid stations with other medics, making sure things stay calm and organized.
Your attention to detail with supplies can make all the difference when it’s time to help someone in the field.

You’ll need specific qualifications and training to become a Combat Medic Specialist. The work involves giving emergency care, facing risks in the field, and knowing how your job stacks up against civilian emergency responders.
You must be a U.S. citizen or permanent resident. You also need to pass the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test.
Good physical fitness and no serious medical conditions are a must.
You’ll provide emergency medical care during combat and other situations. You treat battlefield injuries, evacuate wounded soldiers, and offer basic health care when needed.
It helps to review basic first aid and emergency medical skills. Physical fitness counts, since the training is hands-on and can be tough.
You face dangers from combat—gunfire, explosions, and all the stress that comes with it. The job puts you in high-pressure spots where you have to make quick medical decisions.
As a 68W, you get training similar to an EMT-Intermediate. Paramedics have more advanced skills, but your training gets you ready to provide essential emergency care on the battlefield.
Your salary really comes down to your rank and time in service.
If you’re just starting out as a 68W, you’ll get basic Army pay.
As you move up in rank and stick around longer, your pay goes up too.
You might also get extra benefits and allowances along the way.