PsychNewsDaily Publishers
100 Summit Drive
Burlington, MA, 01803
Telephone: (320) 349-2484
PsychNewsDaily Publishers
100 Summit Drive
Burlington, MA, 01803
Telephone: (320) 349-2484
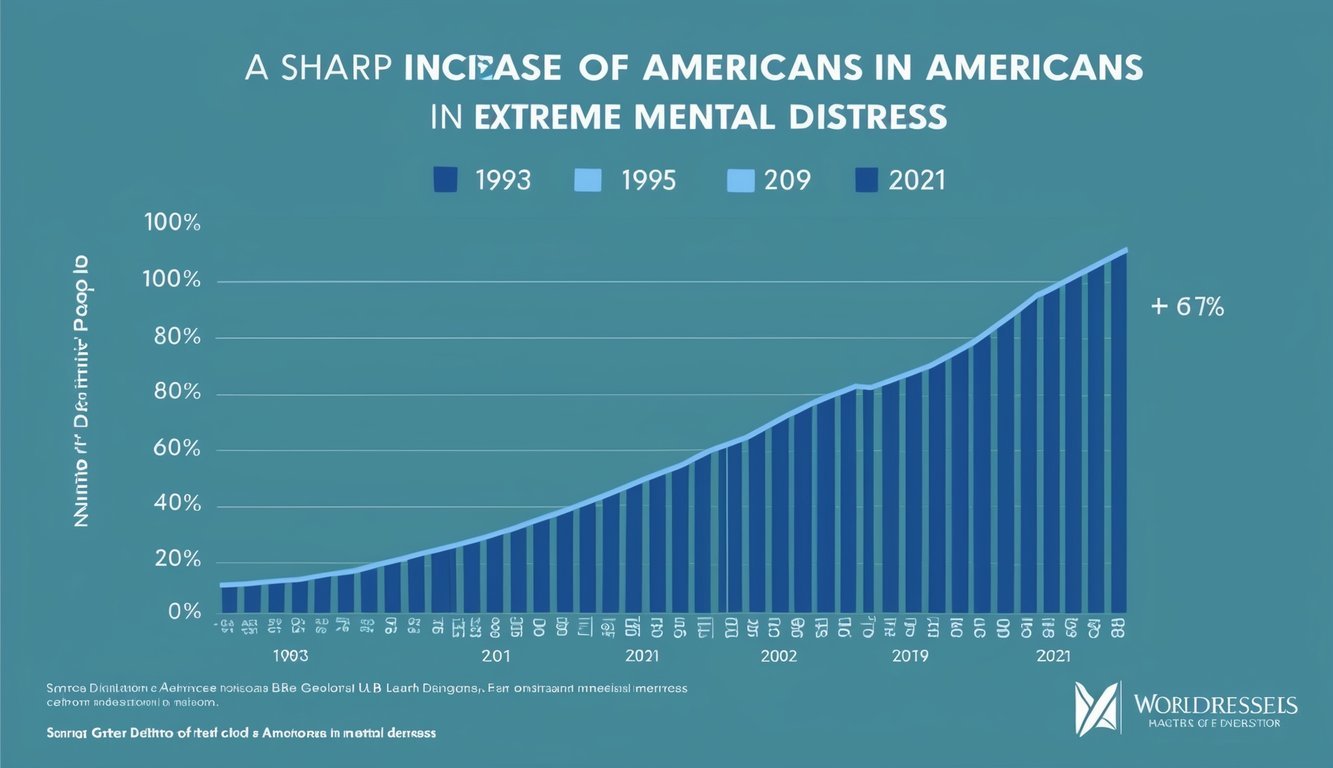
Extreme mental distress among Americans has doubled since 1993, rising from 3.5% to 6.4%, driven by economic instability, social pressures, and increased awareness of mental health issues.
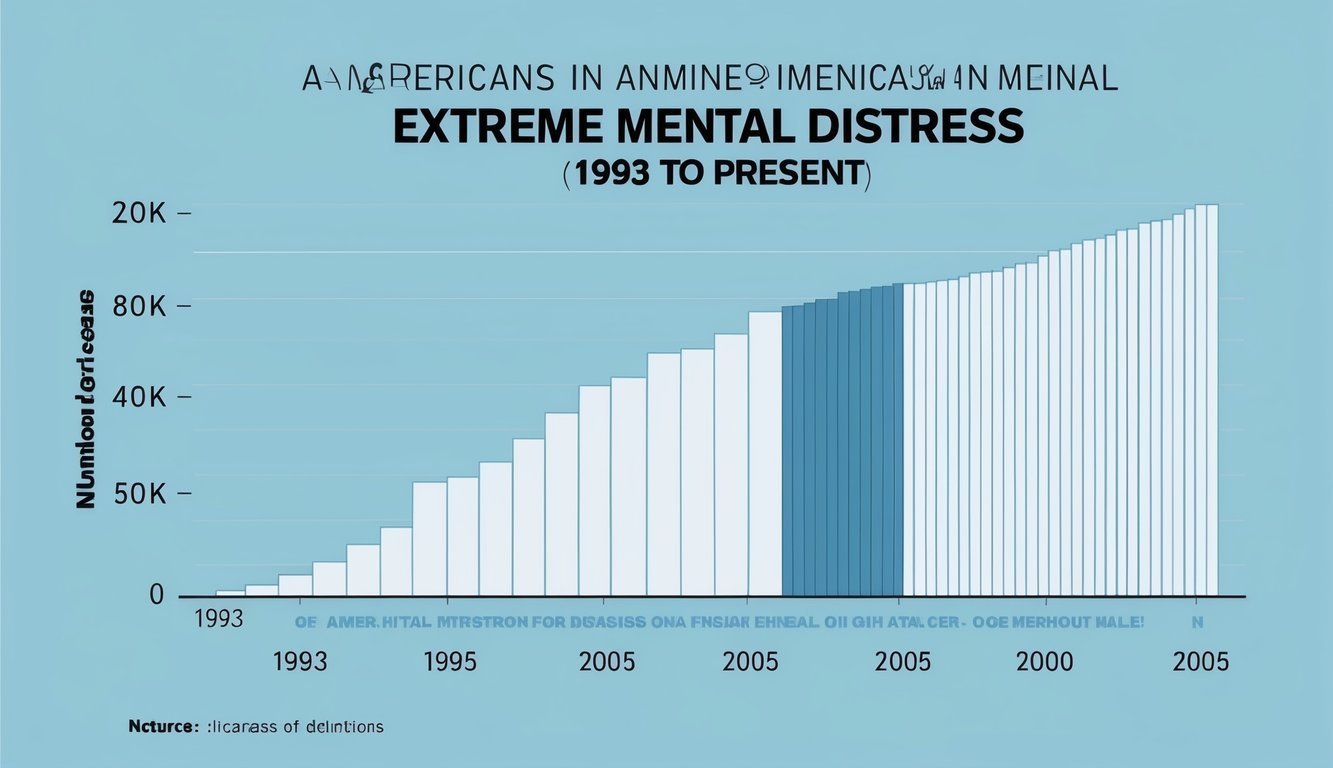
A recent study reveals that extreme mental distress among Americans has doubled since 1993. This significant increase highlights a growing public health concern regarding mental health and the impact of stress on individuals. As society faces various challenges, such as economic shifts and social pressures, mental disorders appear to be more prevalent than ever.
Mental health issues are not just personal struggles; they affect communities and workplaces as well. The rise in extreme mental distress calls attention to the need for better support systems and resources. Understanding this shift can help people recognize the importance of mental well-being and encourage conversations about stress and its effects on daily life.
By exploring the factors contributing to this trend, readers can gain insight into how mental health shapes their world. The discussion aims to inspire awareness and promote healthier coping strategies for dealing with today’s stresses.
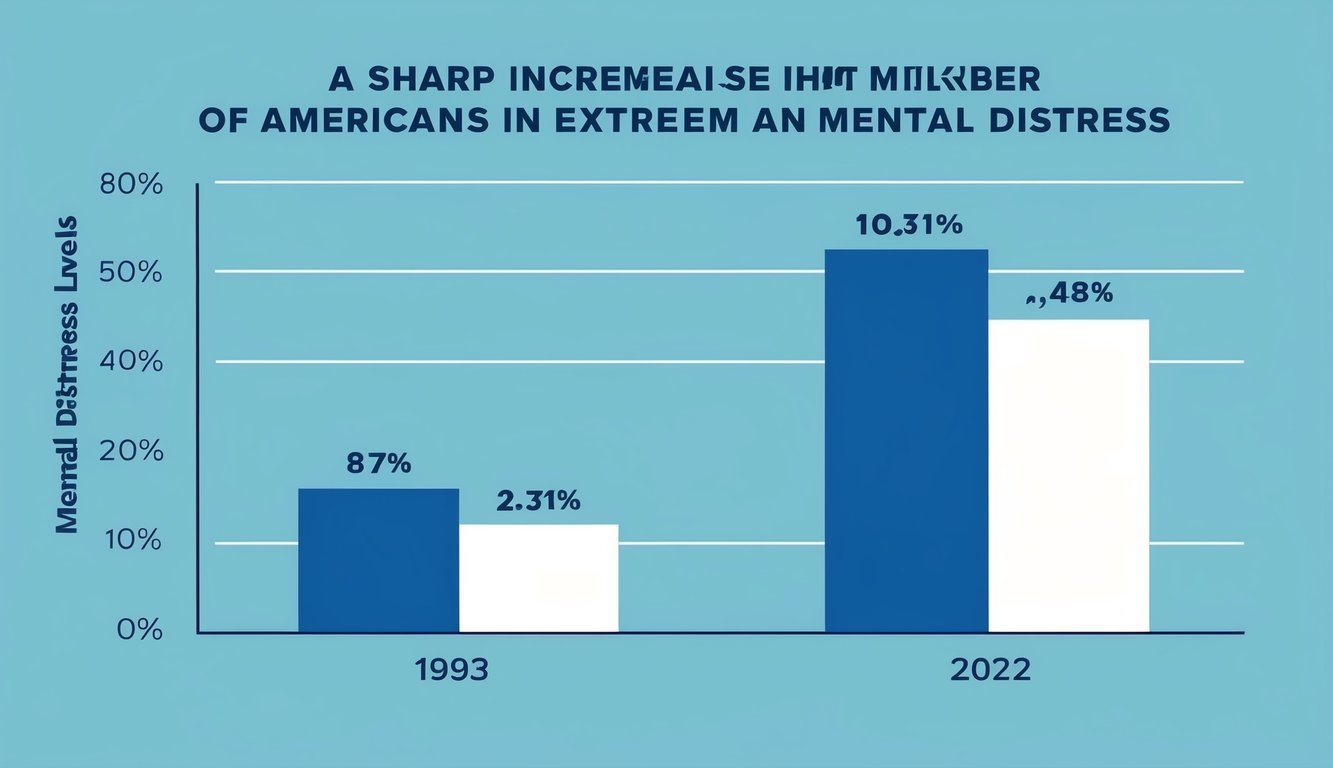
Recent studies show that the number of Americans experiencing extreme mental distress has doubled since 1993. This rise in distress has important implications for public health and highlights various contributing factors.
In 1993, approximately 3.5% of Americans reported extreme mental distress. By 2019, this number rose to 6.4%. This shift reflects a significant change in mental health trends over nearly three decades.
The increase suggests that more people are struggling with conditions like anxiety and depression. The awareness of mental health issues has also grown, leading more individuals to report their feelings.
Factors like societal stressors and economic challenges may play a role. As people face increased demands from work and life, their mental well-being suffers. Thus, it is crucial to consider both the statistics and the context behind them.
Several factors have contributed to the rise in mental distress among Americans. Economic instability, particularly during crises, has heightened stress levels.
Social media exposure may also impact mental health. Constant comparison and online pressure can lead to feelings of inadequacy. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic intensified existing issues, leading to increased anxiety and depression rates.
Furthermore, access to mental health services has improved, allowing individuals to seek help more than before. Despite this progress, stigma around mental health remains, which can prevent people from seeking the support they need.
Addressing these factors is essential for improving mental health outcomes nationwide.
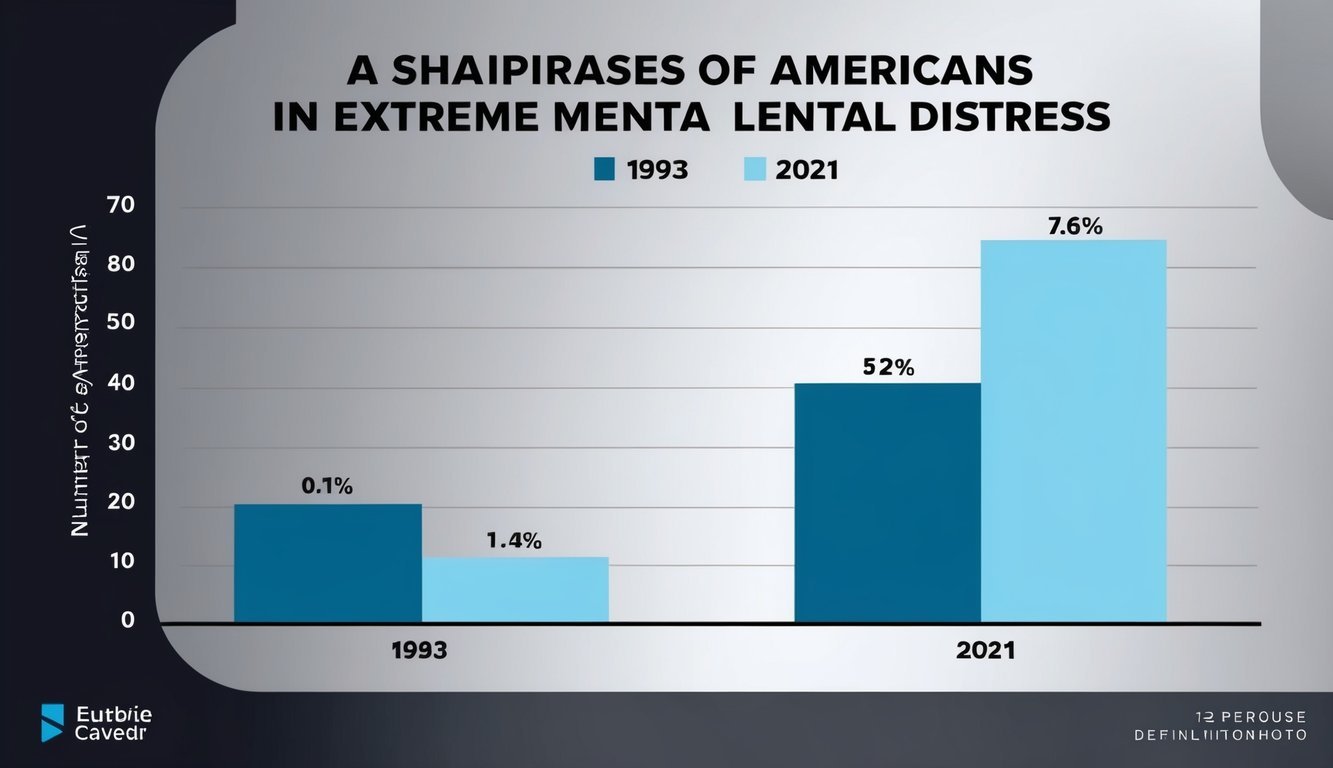
The rise in extreme mental distress among Americans highlights significant challenges for public health services. It suggests a growing need for more resources and better strategies to support those in need. This increase can affect both treatment admissions and overall mental health service effectiveness.
Mental health services face many challenges as the number of individuals in distress rises. The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) has reported increasing demand for accessible mental health care.
Many communities lack adequate resources. Staff shortages are common, and many facilities struggle to hire enough qualified professionals. In addition, state and local budgets often don’t prioritize mental health, leading to funding issues.
These factors lead to longer wait times for patients seeking help, which can worsen conditions. Addressing these challenges is urgent to ensure timely and effective treatment for those affected.
Recent trends show that treatment admissions are also on the rise. With more people experiencing mental distress, many seek help through hospitals and therapy services.
In recent years, several key patterns have emerged:
This trend pressures public health services to enhance their treatment options. Communities need to expand outreach and make mental health services more inclusive. Strengthening these services will be crucial to managing the rising demand and improving outcomes for individuals in distress.
Societal factors play a significant role in mental health outcomes. The influences of race and marital status, along with the economic landscape, impact how individuals experience mental distress.
Research shows that mental health can be affected by race and ethnicity. In the past, non-white individuals reported higher levels of distress compared to whites. By 2019, this trend changed, suggesting that various social factors may contribute to these differences.
Marital status also plays a vital role. People who are married often report better mental health. In contrast, those who are single or divorced may face more challenges. Social support from a partner can reduce feelings of loneliness and stress, positively impacting mental health.
Economic stability is crucial for mental health. Individuals with steady jobs generally experience less stress compared to those who are unemployed. Job loss can lead to financial strain, which often increases feelings of anxiety and depression.
Education level also affects mental well-being. People with higher education levels tend to have more job opportunities and resources, which can lead to better mental health. Discrimination in the workplace can cause additional stress, particularly for marginalized groups. Community violence can exacerbate these issues, creating an environment where mental health struggles flourish.

Substance abuse plays a significant role in mental health issues. Many people facing mental health problems also struggle with substance use disorders. This connection can create a cycle of challenges that affects recovery and overall well-being.
Studies show that nearly half of individuals with mental illnesses also experience a substance use disorder. This relationship is crucial because substances like alcohol, marijuana, and opioids can worsen psychiatric symptoms.
For instance, heroin admissions have increased over the years, as people may turn to drugs to cope with their emotional pain. The combination of substances can lead to increased mental distress.
Those dealing with both conditions may find it harder to get treatment. Integrated care that addresses both mental health and substance abuse is often more effective.
Changes in treatment for substance abuse have affected those with mental health issues. The Treatment Episode Data Set (TEDS) shows a rise in admissions related to heroin and marijuana.
Many treatment centers are now focusing on comprehensive care. This helps individuals address both substance use and mental health needs.
Access to these services varies across regions, and some areas lack adequate resources. Continued investment in treatment services is vital for improving outcomes for those impacted by both substance use and mental health problems.
Accessing mental health care is essential for those facing distress. Many pathways exist, including health services and self-help programs. Understanding these options can help individuals find the support they need.
Getting help through health services is often the first step. Many people rely on health insurance to cover treatment costs. Some insurance plans include coverage for psychiatric care, making it easier for individuals to see a therapist or psychiatrist.
Local clinics and hospitals also provide services. Community mental health centers often offer affordable options for those without insurance. People can find support through hotlines and online resources as well, which can connect them with professional help.
It is important for patients to ask about different treatment options. Medications, therapy, and counseling can all be part of a comprehensive approach to mental health care. Patients should feel empowered to discuss these options with their providers.
Alongside traditional treatment, many emerging therapies offer new hope. Self-help programs have gained popularity due to their accessibility. Online platforms and mobile applications allow users to explore resources at their own pace.
Programs focused on mindfulness, meditation, and exercise can also support mental well-being. These activities help manage stress and promote a positive mindset. Support groups provide another option, allowing individuals to share experiences and learn from each other in a safe space.
As mental health awareness grows, new treatments continue to develop. These include innovative therapy methods and holistic practices, which focus on overall well-being.
This section addresses common questions about the rise in extreme mental distress among Americans. It discusses possible causes, impact on daily life, and available resources for those who need help.
Several factors may contribute to the increase in extreme mental distress. Economic pressures, changes in society, and greater awareness of mental health issues could all play a role. Additionally, the effects of recent events, like the COVID-19 pandemic, may have intensified feelings of distress.
Support for individuals can include therapy, community programs, and medication when appropriate. Encouraging open conversations about mental health can help reduce stigma. People can also practice self-care, such as exercise and healthy eating, to improve their well-being.
Extreme mental distress can affect a person’s ability to work, maintain relationships, and enjoy everyday activities. It can lead to decreased productivity and increased healthcare costs for society. The broader impact includes a ripple effect on families and communities.
Research indicates that certain groups, such as low-education midlife White individuals, have shown higher rates of distress. Additionally, factors like socioeconomic status, race, and age can influence how mental distress affects different populations.
There are numerous resources, including hotlines, support groups, and professional counseling services. Organizations like the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) offer information and assistance. Local community centers may also provide support and programs tailored to specific needs.
Studies suggest a possible link between social media use and mental distress. Spending too much time online can lead to feelings of isolation and anxiety. However, social media can also provide support for some individuals.